Körblein A, Hoffmann W. Background radiation and
cancer mortality in Bavaria:
an ecological analysis.
Arch Environ Occup Health. 2006 May-Jun;61(3):109-14.
The authors investigated a possible association between background gamma
radiation (BGR) and cancer and infant mortality rates. In an in-country
ecological study, they performed a population-weighted linear regression of
cancer (infant) mortality rates on BGR, adjusted for unemployment rate and
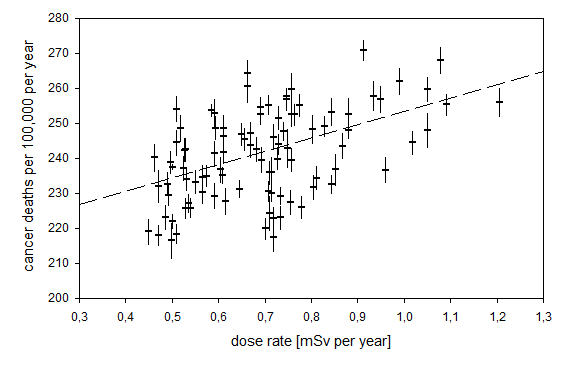
population density. Crude cancer rates showed a highly significant increase with
BGR: 38 excess cases per 100,000 person-years per millisievert/year (p <
.0001).
After adjusting for unemployment rate and population density, the authors found
that the excess absolute risk reduced to 23.6 cases per 100,000 person-years per
mSv/year (p = .0014). The corresponding excess relative risk was 10.2% (95%
confidence interval = 3.9-16.7) per mSv/year. The excess relative risk for
infant mortality rates was 24% (95% confidence interval = 9-42) per mSv/year. The
cancer risk derived from this ecological study is 0.24/Sv, which compares with
an International Commission on Radiological Protection value of 0.05/Sv. However,
because they are based on highly aggregated data, the results should be interpreted with
caution.
download full text here
links:
www.umweltinstitut.org
www.strahlentelex.de
http://www.kinderumweltgesundheit.de/KUG/index2/pdf/themen/Krebs/70001.pdf